 A NASA handout image shows the Robotic Arm on NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander with a sample of martian soil.
A NASA handout image shows the Robotic Arm on NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander with a sample of martian soil.NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander has ceased communications after operating for more than five months, the U.S. space agency reported on Monday.
As anticipated, seasonal decline in sunshine at the robot's arctic landing site is not providing enough sunlight for the solar arrays to collect the power necessary to charge batteries that operate the lander's instruments, NASA said in a statement.
Mission engineers last received a signal from the lander on Nov.2. Phoenix, in addition to shorter daylight, has encountered a dustier sky, more clouds and colder temperatures as the northern Mars summer approaches autumn.
The mission exceeded its planned operational life of three months to conduct and return science data. The project team will be listening carefully during the next few weeks to hear if Phoenix revives and phones home. However, engineers now believe that is unlikely because of the worsening weather conditions on Mars.
While the spacecraft's work has ended, the analysis of data from the instruments is in its earliest stages. "Phoenix has given us some surprises, and I'm confident we will be pulling more gems from this trove of data for years to come," said Phoenix Principal Investigator Peter Smith of the University of Arizona.
Launched Aug. 4, 2007, Phoenix landed May 25, 2008, farther north than any previous spacecraft to land on the Martian surface.
The lander dug, scooped, baked, sniffed and tasted the Red Planet's soil. Among early results, it verified the presence of water-ice in the Martian subsurface, which NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter first detected remotely in 2002.
Phoenix's cameras also returned more than 25,000 pictures from sweeping vistas to near the atomic level using the first atomic force microscope ever used outside Earth.
"Phoenix not only met the tremendous challenge of landing safely, it accomplished scientific investigations on 149 of its 152 Martian days as a result of dedicated work by a talented team," said Phoenix Project Manager Barry Goldstein at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Phoenix's preliminary science accomplishments advance the goal of studying whether the Martian arctic environment has ever been favorable for microbes. Additional findings include documenting a mildly alkaline soil environment unlike any found by earlier Mars missions; finding small concentrations of salts that could be nutrients for life; discovering perchlorate salt, which has implications for ice and soil properties; and finding calcium carbonate, a marker of effects of liquid water.
Phoenix findings also support the goal of learning the history of water on Mars. These findings include excavating soil above the ice table, revealing at least two distinct types of ice deposits; observing snow descending from clouds; providing a mission-long weather record, with data on temperature, pressure, humidity and wind; observations of haze, clouds, frost and whirlwinds; and coordinating with NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to perform simultaneous ground and orbital observations of Martian weather.
"Phoenix provided an important step to spur the hope that we can show Mars was once habitable and possibly supported life," said Doug McCuistion, director of the Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. "With the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory, the Mars Program never sleeps."
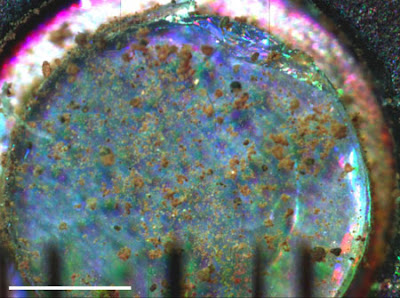 The optical microscope on NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander shows soil sprinkled from the lander's robot arm scoop onto a silicone substrate in this handout image released on June 13, 2008. This is the first sample collected and delivered for instrumental analysis onboard a planetary lander since NASA's Viking Mars missions of the 1970s.
The optical microscope on NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander shows soil sprinkled from the lander's robot arm scoop onto a silicone substrate in this handout image released on June 13, 2008. This is the first sample collected and delivered for instrumental analysis onboard a planetary lander since NASA's Viking Mars missions of the 1970s. View from the Surface Stereo Imager on NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander shows the first impression dubbed Yeti and shaped like a wide footprint -- made on the Martian soil by the robotic arm scoop on Sol 6, the sixth Martian day of the mission, (May 31, 2008). Touching the ground is the first step toward scooping up soil and ice and delivering the samples to the lander's onboard experiments.
View from the Surface Stereo Imager on NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander shows the first impression dubbed Yeti and shaped like a wide footprint -- made on the Martian soil by the robotic arm scoop on Sol 6, the sixth Martian day of the mission, (May 31, 2008). Touching the ground is the first step toward scooping up soil and ice and delivering the samples to the lander's onboard experiments. A white layer visible where the Phoenix Lander robotic arm scooped away the martian soil. NASA said images received on Thursday confirmed that its Phoenix Mars lander has sprinkled a spoonful of Martian soil onto the sample wheel of the spacecraft’s robotic microscope station.
A white layer visible where the Phoenix Lander robotic arm scooped away the martian soil. NASA said images received on Thursday confirmed that its Phoenix Mars lander has sprinkled a spoonful of Martian soil onto the sample wheel of the spacecraft’s robotic microscope station. 



No comments:
Post a Comment